| NEODYMIUM NITRATE HEXAHYDRATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 10045-95-1 14517-29-4 (hydrate) 16454-60-7 (Hexahydrate) |
|
| EINECS NO. | 233-153-9 | |
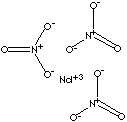
| FORMULA | Nd(NO3)3·6H2O | |
| MOL WT. | 438.34 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | Neodymium (III) Nitrate hexahydrate; | |
| Neodymium Trinitrate hexahydrate; Neodymtrinitrat (German); Trinitrato de neodimio (Spanish); Trinitrate de néodyme (French); | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | red to purple crystals | |
| MELTING POINT |
69 - 71 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Soluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 15.12 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 Special Hazard: OX | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT | Not considered to be a fire hazard | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Hydroscopic. | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION APPLICATIONS |
||
Neodymium is a lustrous, silver-yellow, rare-earth metallic element in the
lanthanide series of group IIIb of the periodic table. Symbol Nd; Aomic number
60; atomic mass 144.24; melting point ca 1,021°C; boiling point ca 3,068°C;
specific gravity 6.80 or 7.004; valence +3; electronic config. [Xe]4f46s². Neodymium tarnishes
in air, forming an oxide form that splits and exposes to further oxidation.
The coated form does not protect the metal from further oxidation (it must be
stored away from contact with air). The metal is also attacked by water and by
acids. Thought it has a hexagonal crystalline structure, but it assumes a
face-centered cubic conformation with specific gravity about 6.8 when heated
above 800°C. Neodymium is not found in nature as the free element but in the
minerals monazite and bastnasite. The metal may be prepared from electrolysis of
its halides or through an ion exchange process. Neodymium is used in coloring
glasses and for doping some glass lasers since it transmits 90% of the blue,
green, and red light rays and no more than 10% of the yellow. Neodymium
compounds include:
|
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
red to purple lump | |
| TREO |
38.0% min |
|
| REO/TREO |
99.5%, 99.99% |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | 5.1 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 1465, 1477 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: O,XI, Risk Phrases: 8-36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 17-26-36 | ||